Advancing Materials. Advancing Outcomes.
The Future of Joint Repair
BioPoly is a revolutionary biomaterial that provides an early stage solution to restore joint function and improve quality of life.


The BioPoly Advantage
A Breakthrough in Cartilage Repair
BioPoly bridges the gap between biological treatments (like microfracture and mACI) and total joint replacements by offering a minimally invasive solution for cartilage repair.
It uses a proprietary material designed to replace only the damaged cartilage, allowing for faster recovery and a return to pain-free motion.
What Is BioPoly®?
BioPoly combines two well-known materials to create a self-lubricated, synthetic cartilage that reduces wear and tear of the natural cartilage, making it ideal for targeted cartilage repair.
- Hyaluronic Acid (HA) for natural joint lubrication.
- Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) for durability and strength.
Key Benefits
Durable design
ensures long-lasting performance and reliability.
Mimics natural cartilage function,
improving joint motion.

Hydrophilic
material promotes smoother articulation.
Learn more
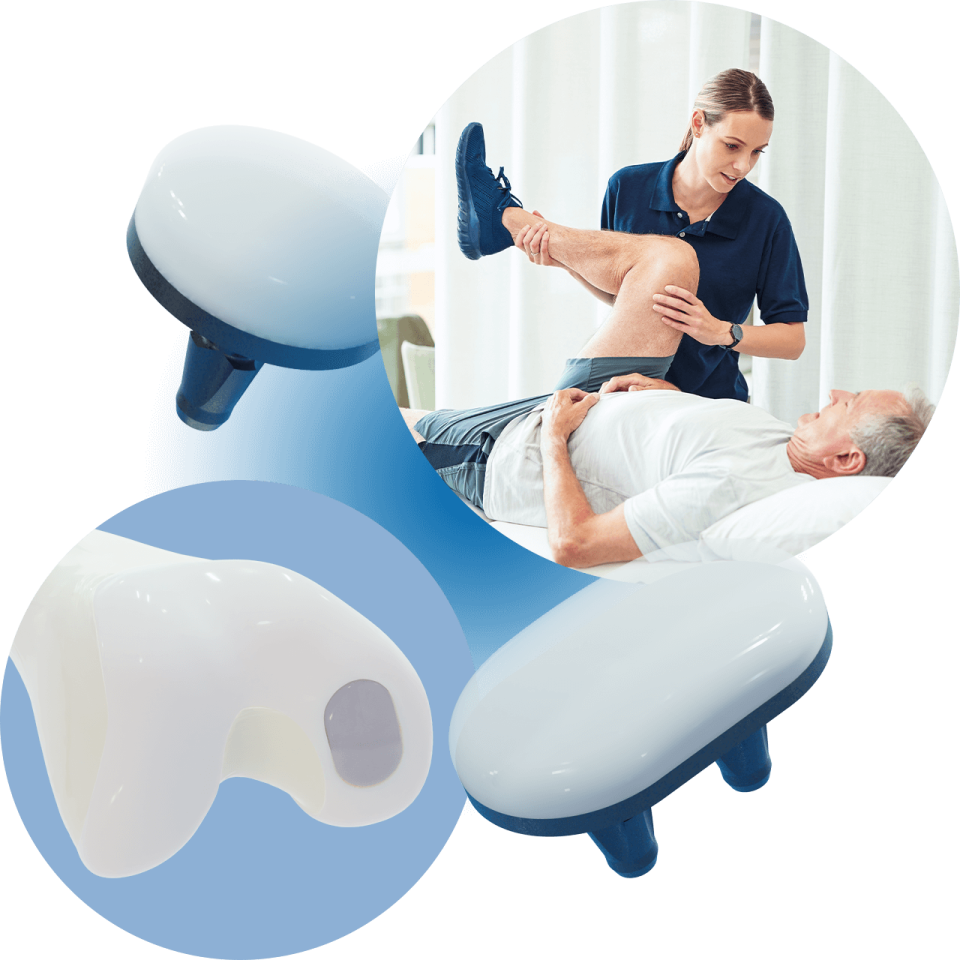
Explore Our Range of BioPoly® Implants
Innovative Solutions for Joint Repair
BioPoly offers a range of advanced orthopedic implants designed to replace cartilage. Each product is manufactured from our patented, self-lubricating material, providing an early-stage solution for patients to regain pain-free movement and restore their active lifestyles. Explore our product lineup to find the right solution for your needs.
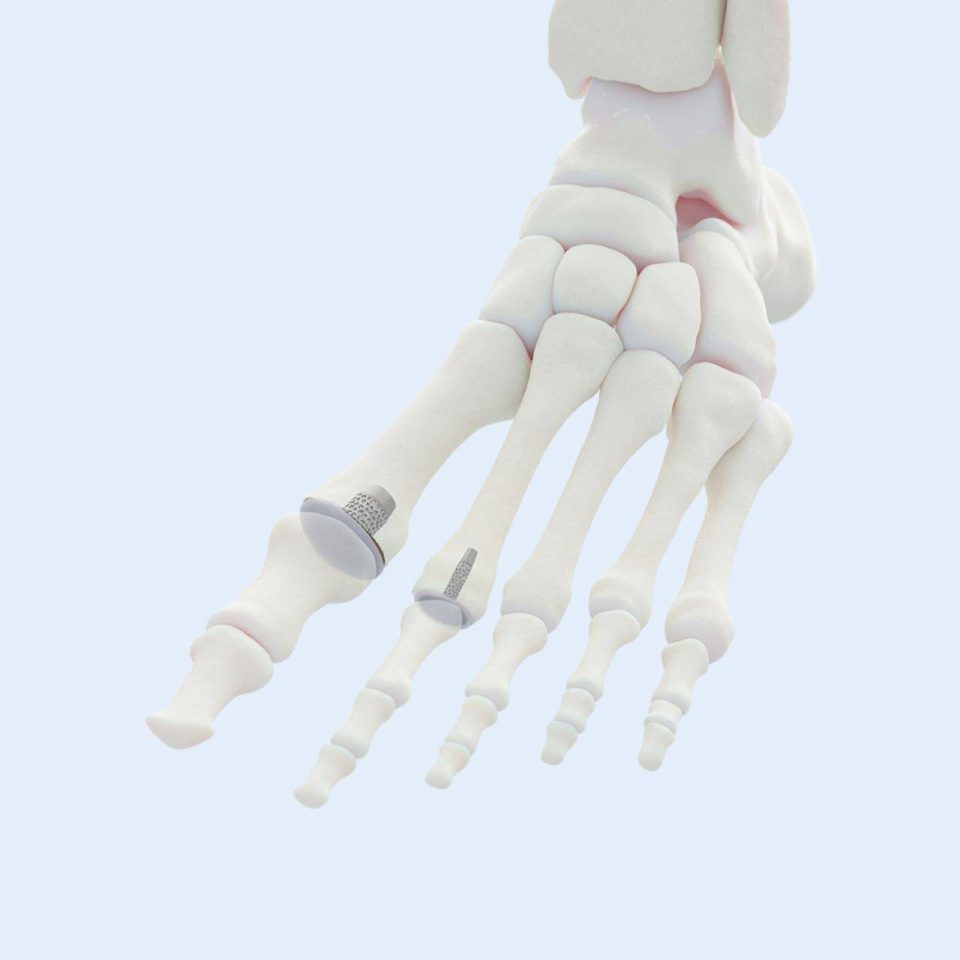
Great & Lesser Toe Implants
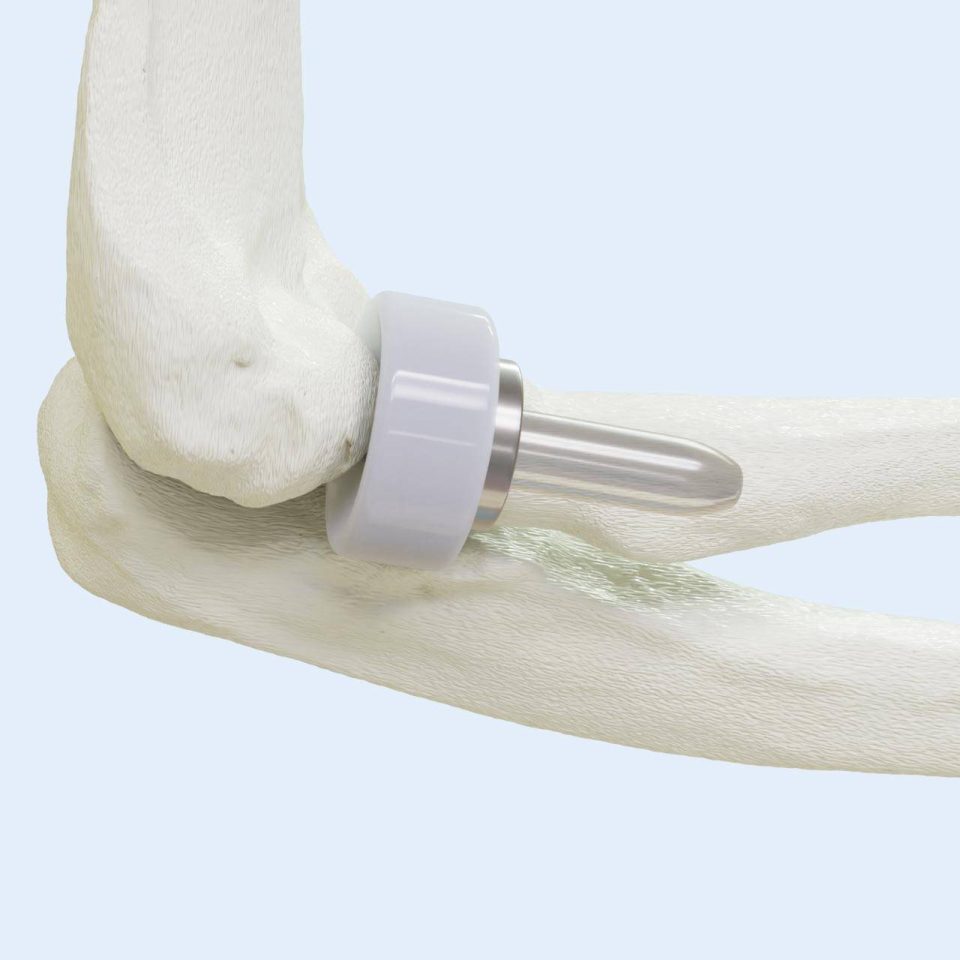
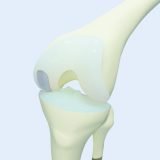
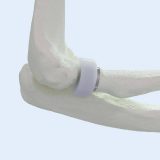
Radial Head Implant

Knee Implant

Products Pipeline
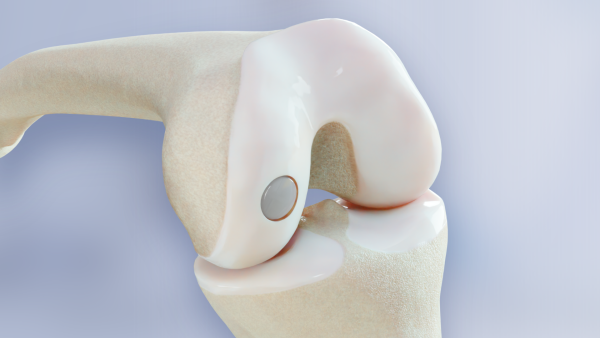
BioPoly® Knee FDA-Approved Clinical Study
Partial Resurfacing Knee Implant is an investigational device and is limited by United States law to investigational use. It is not yet available for commercial sale or use in the U.S.*
Laura H. — BioPoly Patient
About BioPoly®
Revolutionizing Joint Repair for a Pain-Free Future
BioPoly is dedicated to restoring active, pain-free lifestyles by providing game-changing implant solutions for cartilage defects with our revolutionary biomaterial. Founded in Fort Wayne, Indiana, the company has grown from a small startup into a leader in orthopedic material science, developing unique implants that closely mimic the function of natural cartilage.